🖥️ Great Ideas in Computer Architecture: C Arrays, Strings, & Pointers¶
约 312 个字 45 行代码 1 张图片 预计阅读时间 2 分钟 共被读过 次
Instructor: Jenny Song
CS61C su20 - Lecture 3 | 6/26/2020
📚 Review of Last Lecture¶
- C Basics
- Variables, Functions, Control Flow, Syntax.
- Only
0andNULLevaluate toFALSE. - Pointers
- Hold memory addresses (address vs. value).
- Enable efficient code but are error-prone.
- Pass by Value
- C functions pass arguments by value; pointers circumvent this.
🏗️ Struct Clarification¶
Struct Definition¶
C
struct foo { /* fields */ };
struct foo name1; // Declare variable of type struct foo
struct foo* name2; // Pointer to struct foo
Typedef with Struct¶
C
// Method 1
struct foo { /* fields */ };
typedef struct foo bar;
bar name1;
// Method 2 (combine definition and typedef)
typedef struct foo { /* fields */ } bar;
bar name1;
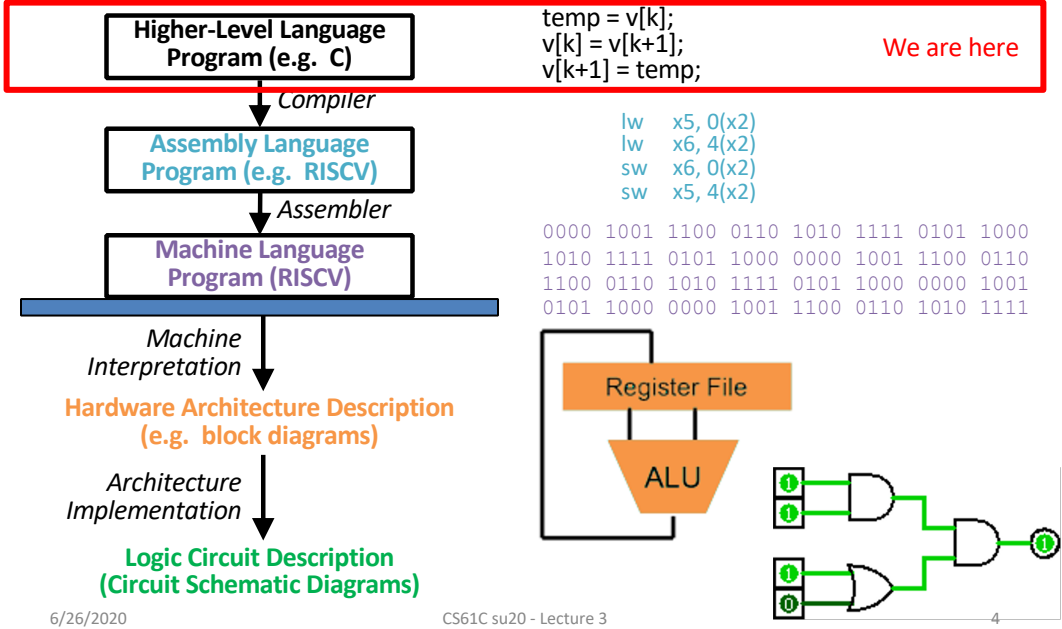
🌟 Great Idea #1: Levels of Representation/Interpretation¶
📜 Agenda¶
- C Operators
- Arrays
- Strings
- More Pointers (Arithmetic, Misc)
🔢 C Operators¶
Operator Precedence Table¶
| Precedence | Operator | Description | Associativity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ++, -- (post) | Postfix increment/decrement | Left-to-right |
| 1 | () | Function call | |
| 1 | [] | Array subscripting | |
| 2 | ++, -- (pre) | Prefix increment/decrement | Right-to-left |
| 2 | *, & | Dereference, Address-of |
Common Pitfalls¶
- Assignment vs. Equality
- Operator Binding
-x & 1 == 0→x & (1 == 0)(not(x & 1) == 0).
📦 Arrays¶
Basics¶
- Pitfalls: No bounds checking! Accessing
ar[n] where n >= 2 causes undefined behavior. Arrays vs. Pointers¶
- Similarities:
- Differences:
sizeof(ar)returns array size;sizeof(ptr)returns pointer size.- Arrays cannot be reassigned (
ar = new_arrayis invalid).
Example: Zeroing an Array¶
C
// Method 1: Array notation
for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) ar[i] = 0;
// Method 2: Pointer arithmetic
for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) *(ar + i) = 0;
// Method 3: Pointer traversal
for (int* p = ar; p < ar + SIZE; p++) *p = 0;
📜 Strings in C¶
- Definition: Null-terminated char array.
- Common Functions (
#include <string.h>): strlen(s): Returns length (excluding\0).strcmp(s1, s2): Returns0if equal.strcpy(dest, src): Copiessrctodest.
Example¶
-
strcmp(s1, s2) == 0 → 1 (true).-
s1 == s2 → 0 (compares addresses, not content). 🎯 Pointers¶
Pointer Arithmetic¶
- Rules:
ptr + naddsn * sizeof(*ptr)to the address.- Valid operations:
ptr ± int, subtract pointers, compare pointers. - Example:
Pointers to Pointers¶
C
void IncrementPtr(int** h) { *h = *h + 1; }
int A[] = {50, 60, 70};
int* q = A;
IncrementPtr(&q); // q now points to A
🧩 Struct Alignment¶
- Rules:
- Members aligned to their size (e.g.,
intaligned to 4 bytes). - Padding added to meet alignment requirements.
Example¶
C
struct hello {
int a; // 4 bytes
char b; // 1 byte (+3 padding)
short c; // 2 bytes
char* d; // 4 bytes
char e; // 1 byte (+3 padding)
};
// Total size: 4 + (1+3) + 2 + 4 + (1+3) = 16 bytes
🚨 Common Pitfalls & Tips¶
- Uninitialized Pointers:
- Array Decay: When passed to functions, arrays decay to pointers (losing size info).
- Null Terminator: Forgot
\0in strings?strlenmay read garbage!
✨ Key Takeaways:
- Arrays and pointers are powerful but error-prone.
- Always manage memory carefully and use sizeof() for portability.
- Understand alignment to optimize struct layouts!