🧠 C Memory Management & Usage - Comprehensive Notes¶
约 411 个字 38 行代码 4 张图片 预计阅读时间 3 分钟 共被读过 次
📚 Table of Contents¶
- C Memory Layout
- Addressing & Endianness
- Dynamic Memory Allocation
- Common Memory Problems
- Linked List Example
- Memory Fragmentation & K&R Algorithm
- Debugging Tools
🗺️ C Memory Layout¶
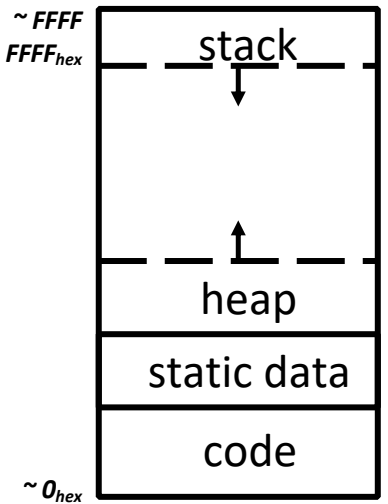
Program Address Space¶
- 4 Regions:
1. Stack 📥- Stores local variables (declared inside functions).
- Grows downward.
- Freed when function returns.
- Example:
int x = 5;insidemain().
-
Heap 🧱
- Dynamically allocated via
malloc(),calloc(),realloc(). - Grows upward.
- Must be explicitly freed with
free(). - Example:
int *arr = malloc(10 * sizeof(int));.
- Dynamically allocated via
-
Static Data 🌐
- Stores global/static variables and string literals.
- Does not grow/shrink.
- Example:
char *str = "hello";(string literal in static data). - ⚠️
char str[] = "hello";stores the array on the stack!
-
Code 📜
- Contains compiled machine code.
- Read-only and immutable.
🔢 Addressing & Endianness¶
Key Concepts¶
- Byte-Addressed Machines: Each address points to a unique byte.
- Word-Addressed Machines: Each address points to a word (group of bytes).
- Endianness: Order of bytes in multi-byte data types.
Types of Endianness¶
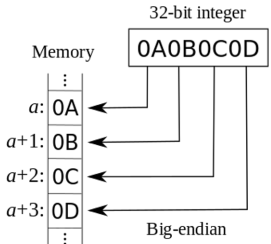
- Big Endian 🐘
- Most significant byte at lowest address.
- Example:0x12345678stored as12 34 56 78. - Little Endian 🐭
- Least significant byte at lowest address.
- Example:0x12345678stored as78 56 34 12.
Example: Integer 28 (0x0000001C)¶
- Big Endian:
00 00 00 1C - Little Endian:
1C 00 00 00
💥 Dynamic Memory Allocation¶
Functions¶
malloc(n)
- Allocatesnbytes of uninitialized memory.
- Example:
calloc(n, size)
- Allocatesn * sizebytes initialized to zero.
- Example:
realloc(ptr, new_size)
- Resizes existing memory block.
- May move the block to a new address.
- Example:
free(ptr)
- Releases memory.
- ⚠️ Never free:- Stack variables.
- Already freed memory.
- Middle of a block (e.g.,
free(arr + 1)).
🚨 Common Memory Problems¶
1. Using Uninitialized Values¶
2. Using Memory You Don’t Own¶
- Example 1: Returning a stack-allocated array.
- Example 2: Buffer overflow.
3. Freeing Invalid Memory¶
- Double Free:
- Freeing Stack Variable:
4. Memory Leaks¶
- Example: Overwriting a pointer before freeing.
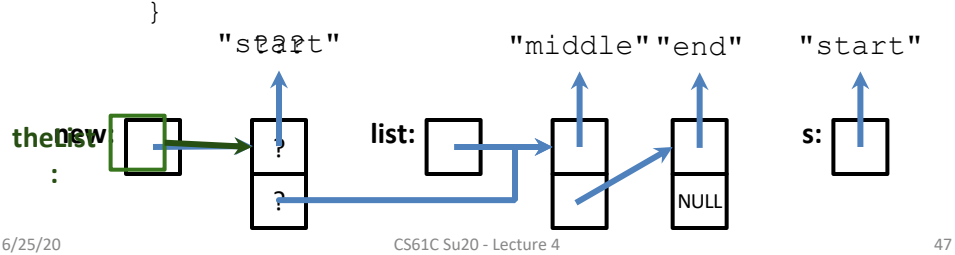
🔗 Linked List Example¶
Node Structure¶
Adding a Node¶
C
struct Node* addNode(char *s, struct Node *list) {
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->value = (char*)malloc(strlen(s) + 1); // +1 for '\0'
strcpy(newNode->value, s);
newNode->next = list;
return newNode;
}
Freeing a Node¶
C
void freeList(struct Node *list) {
while (list != NULL) {
struct Node *temp = list;
list = list->next;
free(temp->value); // Free the string
free(temp); // Free the node
}
}
Visualization¶
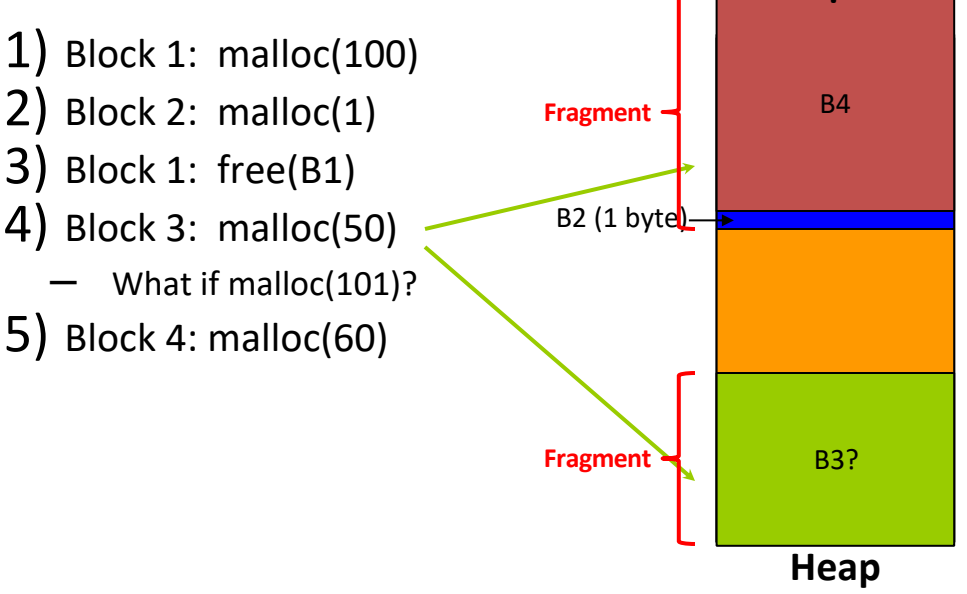
🧩 Memory Fragmentation & K&R Algorithm¶
Fragmentation Example¶
K&R Allocation Strategy¶
- Free List: Linked list of free memory blocks.
- Merging Adjacent Blocks:
free()combines adjacent free blocks. - Allocation Policies:
- First Fit: Use the first block that fits.
- Best Fit: Use the smallest block that fits.
- Next Fit: Resume search from last position.
🛠️ Debugging Tools¶
- Valgrind 🧪: Detects memory leaks, invalid accesses, and more.
- Example Output:
📌 Summary¶
- Stack: Local variables, LIFO.
- Heap: Dynamic, manually managed.
- Static Data: Globals & literals.
- Code: Immutable.
- Common Pitfalls: Leaks, invalid accesses, uninitialized values.
- Golden Rule: Always pair
malloc()withfree()! 🛑