Memory Hierarchy - Lecture Notes 📚¶
约 600 个字 14 行代码 1 张图片 预计阅读时间 3 分钟 共被读过 次
Key Concepts 🧠¶
The CPU-Memory Gap ⚡¶
- Problem: Widening gap between CPU speed and memory/disk access times.
- Memory Wall/Von Neumann Bottleneck: Performance gap between computation speed and data storage.
- Solutions:
- Memory Hierarchy (Covered in 213)
- Parallelism (346, 418)
- Computation Migration (346, 7xx?)
Memory Abstraction 🏗️¶
RAM (Random-Access Memory) 💾¶
- Key Features:
- Packaged as a chip or embedded in processors.
- Basic unit: cell (1 bit per cell).
- Varieties:
- SRAM (Static RAM):
- 6-8 transistors/bit.
- Faster (1x access time), no refresh needed.
- Expensive (100x DRAM cost).
- Used for cache memories.
- DRAM (Dynamic RAM):
- 1 transistor + 1 capacitor/bit.
- Slower (10x access time), requires periodic refresh.
- Cheaper (1x DRAM cost).
- Used for main memories and frame buffers.
| Feature | SRAM | DRAM |
|---|---|---|
| Transistors/bit | 6-8 | 1 |
| Access Time | 1x | 10x |
| Refresh Needed? | No | Yes |
| Cost | 100x | 1x |
| Applications | Cache | Main Memory |
Locality of Reference 🎯¶
- Principle: Programs tend to access data/instructions near recently used addresses.
- Types:
1. Temporal Locality: Recently used items are likely to be reused soon.- Example: Loop variable
sumaccessed repeatedly.
2. Spatial Locality: Nearby addresses are accessed close in time. - Example: Iterating through an array in stride-1 pattern.
- Example: Loop variable
Example 1: Locality Analysis 🔍¶
C
int sum_array_rows(int a[M][N]) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
sum += a[i][j];
return sum;
}
- Locality:
- Spatial: Array accessed in row-major order (stride-1).
- Temporal: Variable
sum accessed each iteration.- Answer: ✅ Good locality (both spatial and temporal).
Example 2: Poor Locality ❌¶
C
int sum_array_cols(int a[M][N]) {
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
sum += a[i][j];
return sum;
}
- Locality:
- Stride-N pattern (non-contiguous memory access).
- Answer: ❌ Poor locality unless
M is very small. Memory Hierarchy 🗃️¶
- Goal: Create an illusion of large, fast memory using smaller, faster storage layers.
- Caches:
- Faster, smaller storage acting as a staging area for slower, larger storage.
- Hit: Data found in cache.
- Miss: Data fetched from lower levels.
- Types of Misses:
- Cold (Compulsory) Miss: First access to a block.
- Capacity Miss: Working set exceeds cache size.
- Conflict Miss: Data maps to same cache block (e.g., blocks 0, 8, 0, 8...).
Cache Types 📦¶
| Cache Type | Cached | Location | Latency (cycles) | Managed By |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registers | 4-8 byte words | CPU core | 0 | Compiler |
| L1 Cache | 64-byte blocks | On-Chip L1 | 4 | Hardware |
| L2 Cache | 64-byte blocks | On-Chip L2 | 10 | Hardware |
| Virtual Memory | 4-KB pages | Main Memory | 100 | Hardware + OS |
| Disk Cache | Disk sectors | Disk Controller | 100,000 | Disk Firmware |
Storage Technologies 💽¶
Magnetic Disks 🛠️¶
- Components:
- Platters, tracks, sectors.
- Access Time:
- Seek Time: Position head over cylinder (3-9 ms).
- Rotational Latency: Wait for sector to rotate under head (4 ms @ 7200 RPM).
- Transfer Time: Read data (0.02 ms for 400 sectors/track).
Example: Disk Access Time Calculation ⏳
- Given: 7200 RPM, 9 ms seek time, 400 sectors/track.
- Total Access Time:
SSDs vs HDDs 🔄¶
| Feature | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Faster (no moving parts) | Slower (mechanical latency) |
| Durability | Limited writes (wear leveling) | No wear-out from writes |
| Cost | 1.67x more expensive (2023) | Cheaper bulk storage |
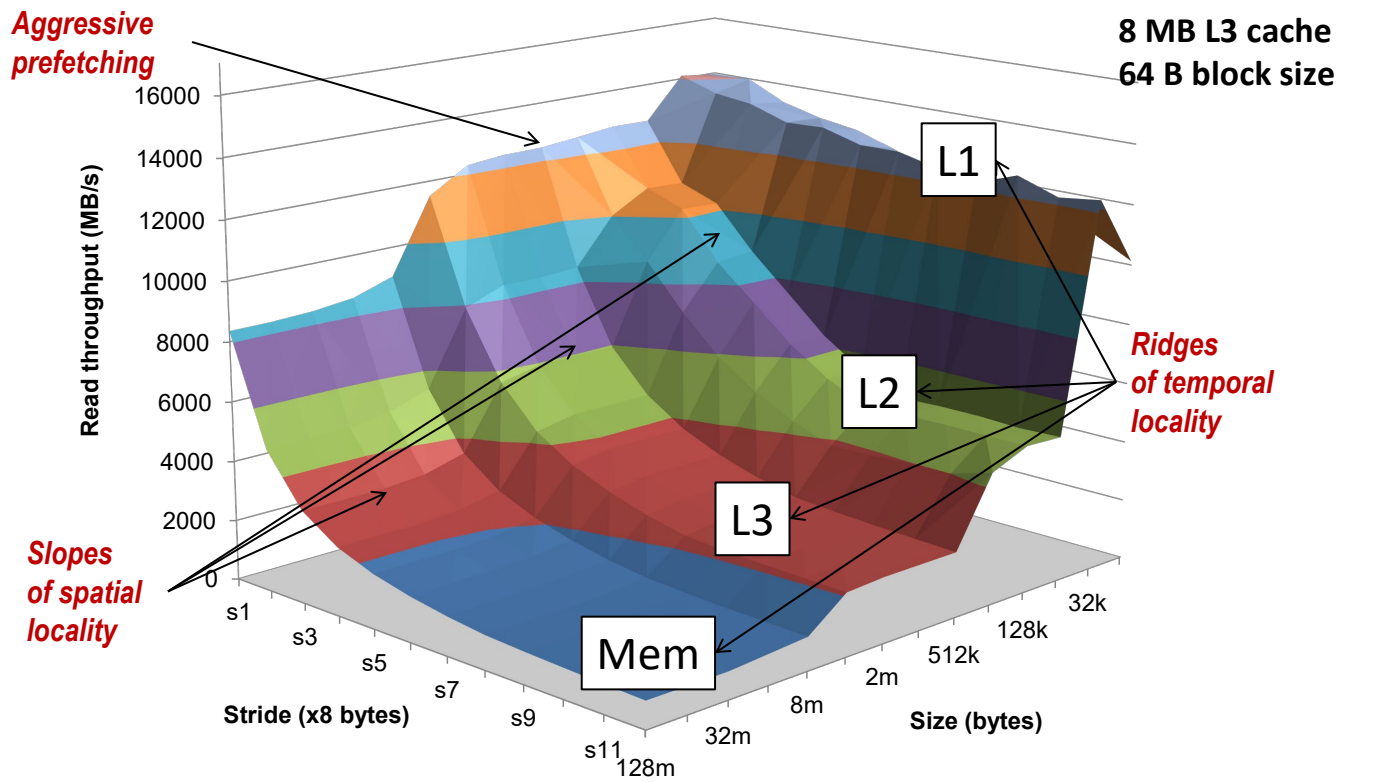
Memory Mountain 🏔️¶
- Read Throughput: Measures bandwidth (MB/s) as a function of spatial/temporal locality.
- Core i7 Haswell Results:
- L1: 32 KB, 4 cycles.
- L2: 256 KB, 10 cycles.
- L3: 8 MB, 40-75 cycles.
- Key Insight: Larger strides reduce spatial locality, lowering throughput.
Trends 📈¶
- SRAM/DRAM Scaling:
- SRAM limited by transistor density.
- DRAM limited by capacitor aspect ratio.
- Storage:
- Flash memory advancing faster than DRAM/HDD.
- 3D NAND allows stacking cells vertically (100+ layers).
Historical Data 📊¶
| Year | SRAM $/MB | DRAM $/MB | Disk $/GB |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1985 | $2,900 | $880 | $100,000 |
| 2015 | $320 | $0.02 | $0.03 |
Quiz Time! 🧩¶
-
Q: Which RAM type uses capacitors?
A: DRAM (Dynamic RAM). -
Q: What type of cache miss occurs due to limited cache size?
A: Capacity miss. -
Q: Which loop permutation improves spatial locality in a 3D array?
A: Inner loop iterates over contiguous memory (e.g.,for jinner loop).
Source: Bryant and O'Hallaron, Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective, Third Edition 📖