📚 Machine-Level Programming IV: Data¶
约 226 个字 40 行代码 7 张图片 预计阅读时间 2 分钟 共被读过 次
15-213/15-513: Introduction to Computer Systems
6th Lecture, Sept 12, 2024
🧮 Arrays¶
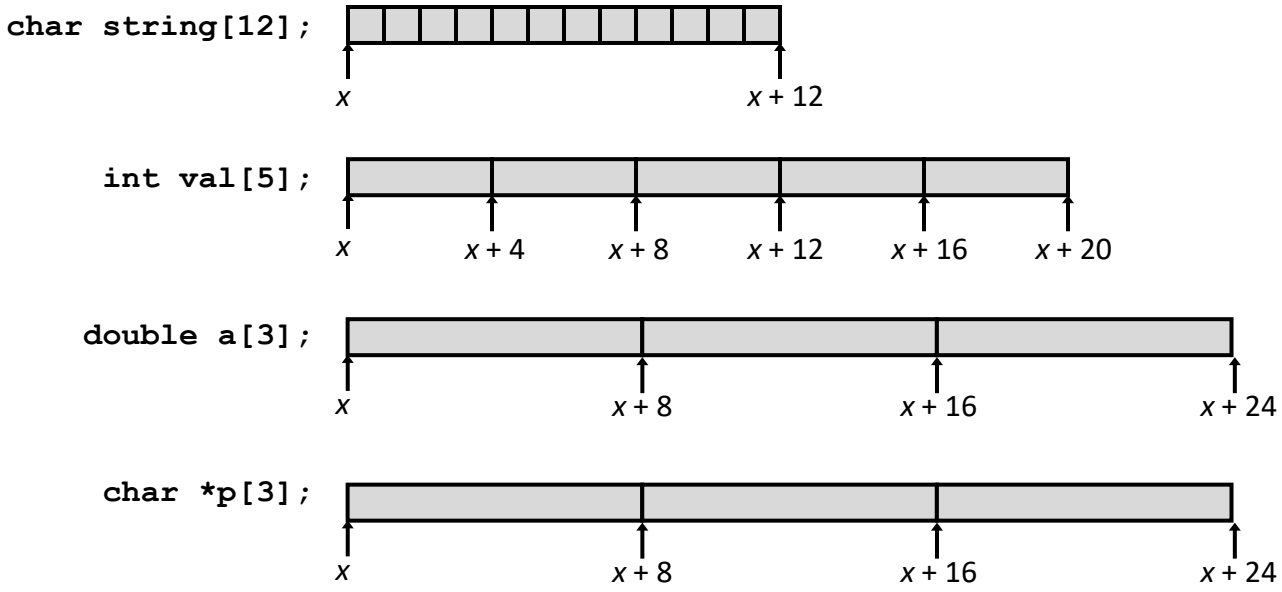
One-Dimensional Arrays¶
- Declaration:
T name[Length]; - Contiguously allocated region of
Length * sizeof(T)bytes. - Access:
- Identifier
nameacts as a pointer to element 0. - Example:
valtranslates to*(val + 4).
Example: Array Allocation¶
- Memory layout (20-byte block):

Multi-Dimensional (Nested) Arrays¶
- Declaration:
T A[R][C]; - Row-Major Order: Elements stored row-wise.
- Row Access:
A[i]starts atA + i * (C * sizeof(T)). - Element Access:
A[i][j]address =A + (i * C + j) * sizeof(T).
Example: 2D Array¶
- Memory layout:
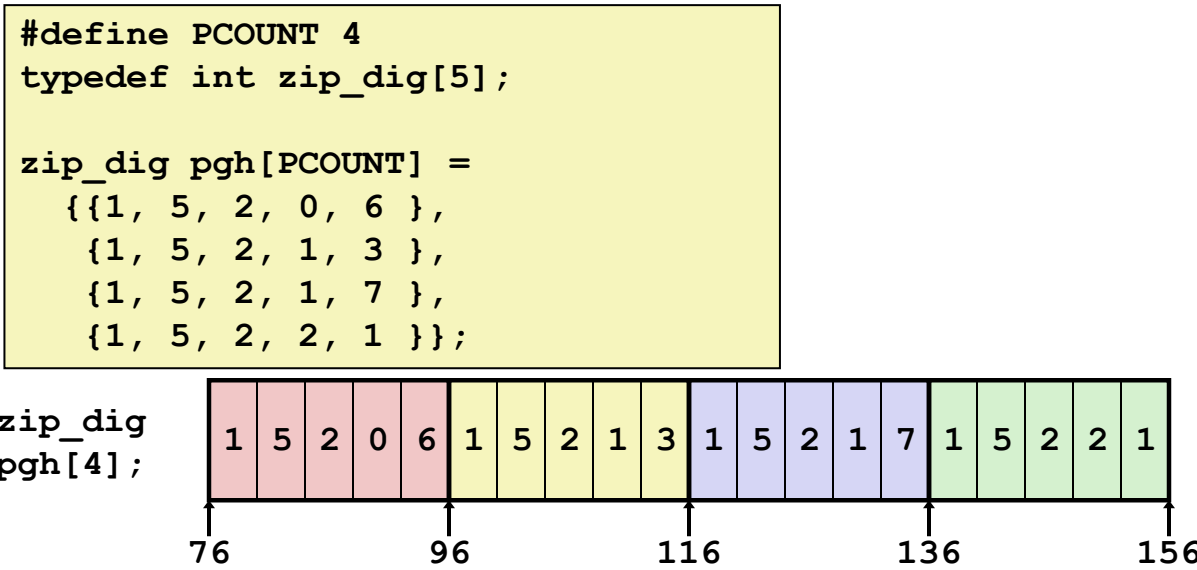
Assembly for Element Access¶
Text Only
# Access pgh[index][dig]
leaq (%rdi, %rdi, 4), %rax # 5 * index
addl %rax, %rsi # 5*index + dig
movl pgh(, %rsi, 4), %eax # Mem[pgh + 4*(5*index + dig)]
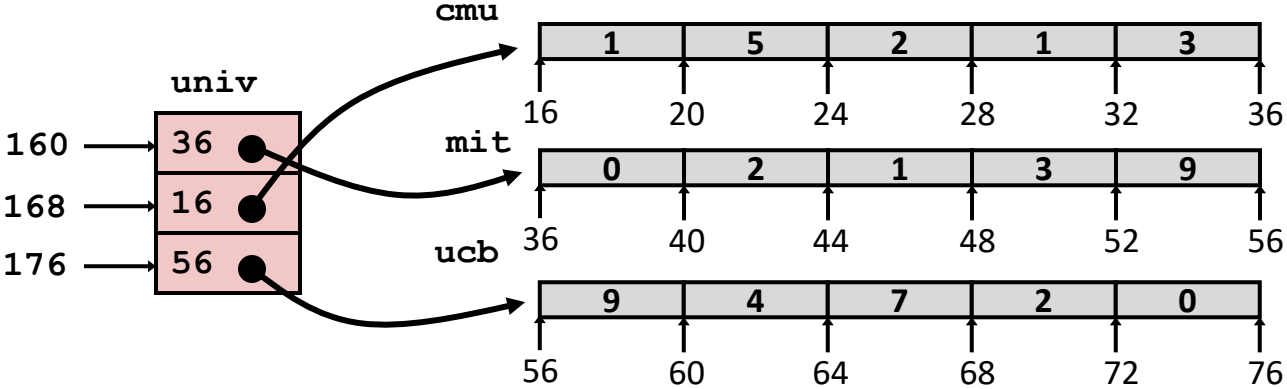
Multi-Level Arrays¶
Element Access¶
- Requires two memory reads:
🏗️ Structures¶
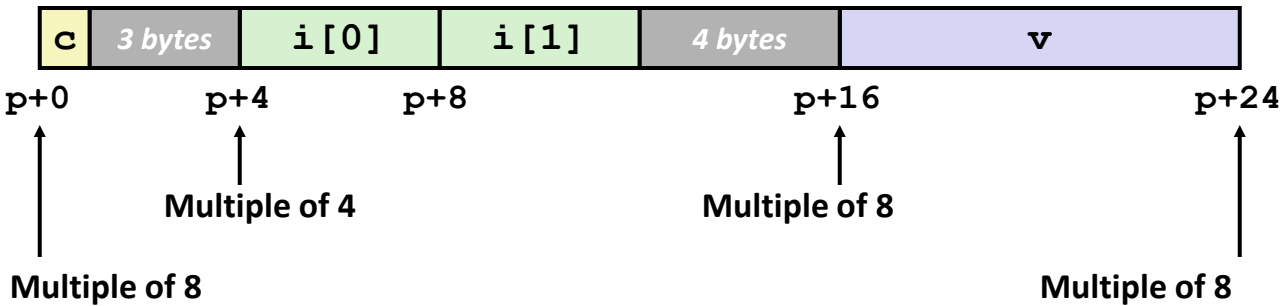
Memory Allocation & Alignment¶
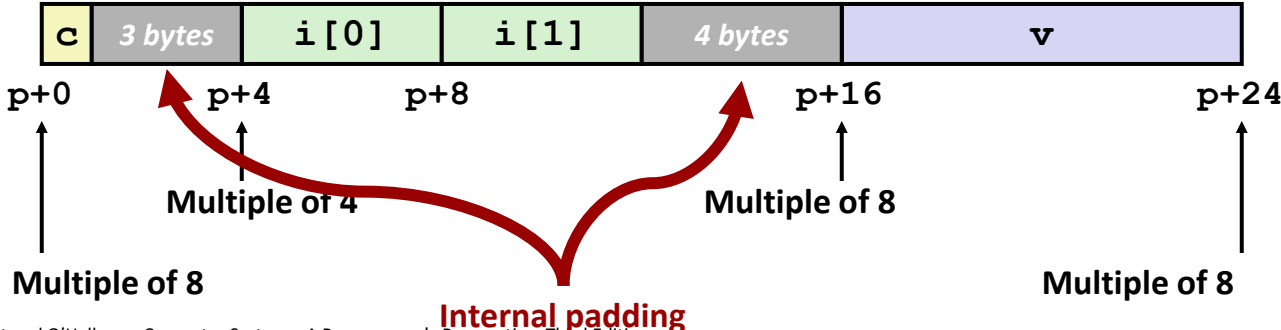
Structure Padding Example¶
- Memory layout (each element padded to 24 bytes):
Linked List Example¶
- Assembly:
Text Only
.L11:
addq $1, %rax # len++
movq 24(%rdi), %rdi # r = Mem[r + 24]
testq %rdi, %rdi
jne .L11
🎯 Floating Point¶
Basics¶
- Registers: XMM registers (
%xmm0,%xmm1, ...) for FP arguments/results. - Operations:
Example: FP Function¶
- Assembly:
Text Only
movapd %xmm0, %xmm1 # Copy v
movsd (%rdi), %xmm0 # x = *p
addsd %xmm0, %xmm1 # t = x + v
movsd %xmm1, (%rdi) # *p = t
📝 Quiz & Examples¶
Understanding Pointers & Arrays #1¶
| Decl | Comp | Bad | Size | A1/A2 Comp | Bad | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
int A1 | Y | N | 12 | Y | N | 4 |
int *A2 | Y | N | 8 | Y | Y | 4 |
Array Access Example¶
🔍 Summary¶
- Arrays: Contiguous memory, index arithmetic for access.
- Structures: Compiler-managed padding for alignment.
- Floating Point: XMM registers and SIMD operations.
⚠️ Key Reminder: Always consider alignment and pointer arithmetic nuances in low-level code!