1 why parallelism
🕰️ Historical Context of Parallel Computing¶
约 165 个字 6 张图片 预计阅读时间 1 分钟 共被读过 次
■ 1970s–2000s: Supercomputers & Databases¶
- C.mmp at CMU (1971): 16 PDP-11 processors.

- Cray XMP (1984): 4 vector processors.

- Sun Enterprise 10000 (1997): 16 UltraSPARC-II processors.

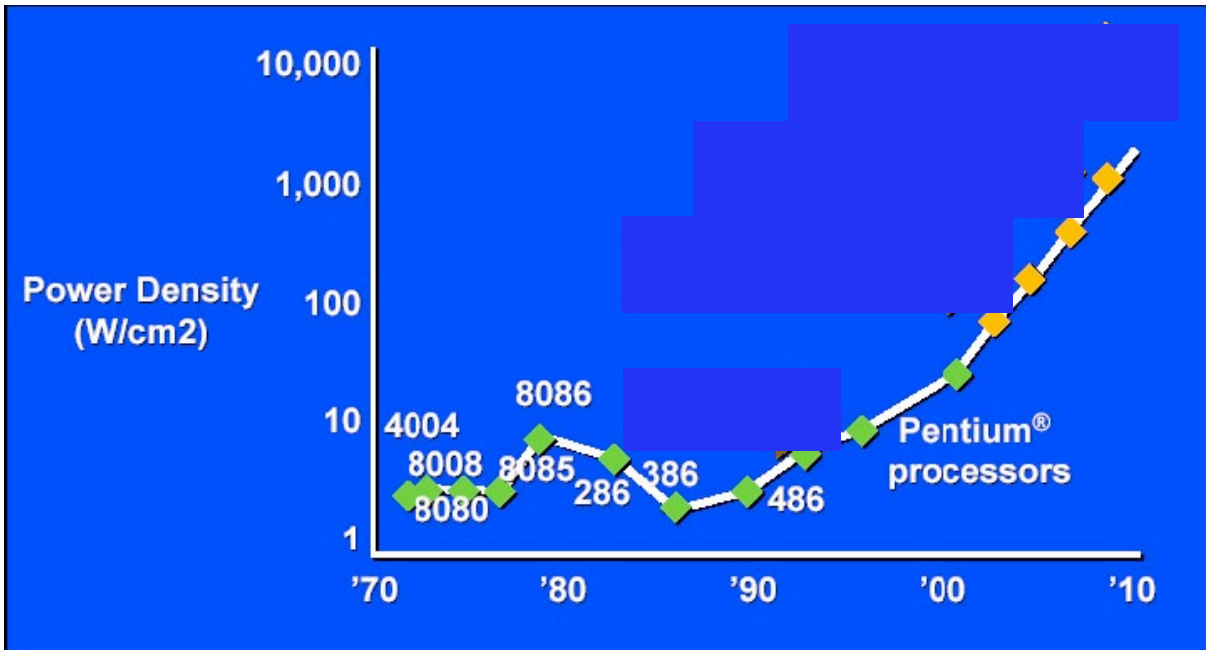
■ Inflection Point (2004)¶
💡 Key Concepts¶
■ Speedup Formula¶
\[\text{Speedup}(P) = \frac{\text{Execution Time (1 processor)}}{\text{Execution Time (P processors)}}\]
Demo Observations:
1. Demo 1: Communication limits speedup.
2. Demo 2: Work imbalance reduces efficiency.
3. Demo 3: Communication dominates computation.
🖥️ Modern Parallel Hardware¶
■ Apple Products¶
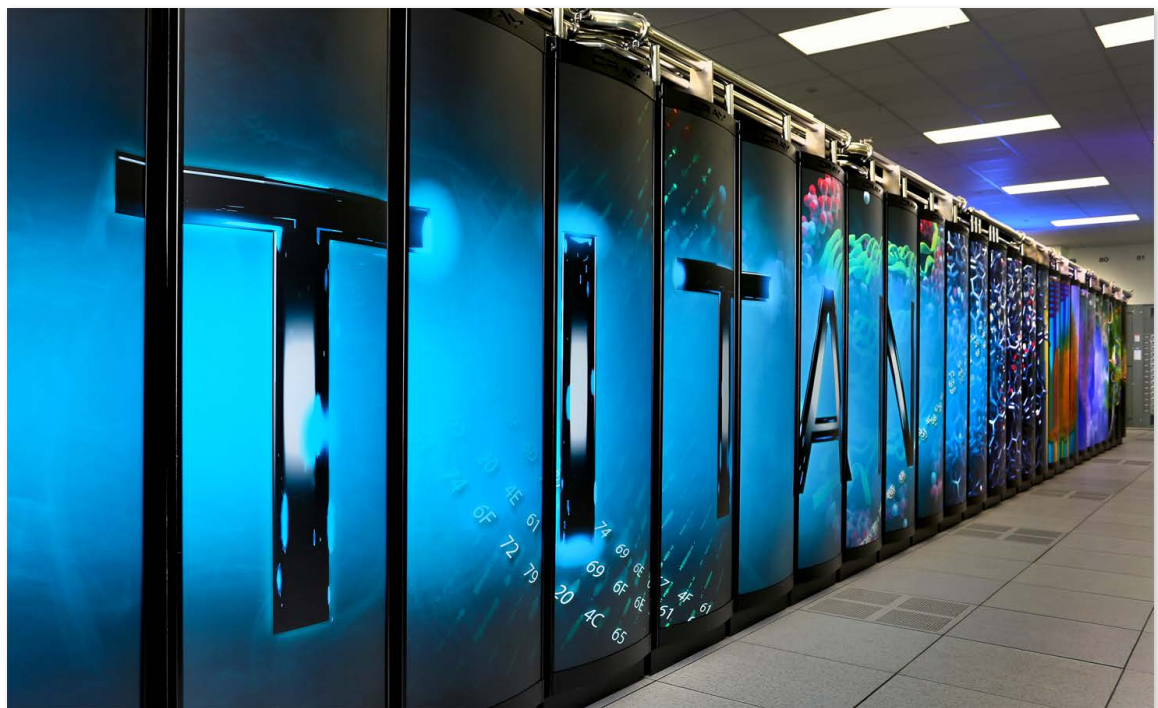
■ Supercomputers¶
🧩 Course Themes¶
- Scaling Parallel Programs:
- Decomposition, work assignment, communication. - Hardware Efficiency:
- Performance vs. cost vs. power. - Post-2004 Shift:
- Maximize performance per Watt instead of raw speed.
🚨 Key Takeaways¶
- Single-thread performance growth is stagnant → Parallelism is essential.
- Writing parallel code is challenging but unlocks immense computational power.
- Efficiency matters: 2x speedup on 1010 processors is not impressive.
📢 Welcome to 15-418!